76
3)
The discharge well penetrates and receives water from the entire
thickness of the aquifer.
4)
The transmissivity is constant at all times and at all places.
5)
The well has an infinitesimal diameter.
6)
Water removed from storage is discharged instantaneously with decline
in the head.
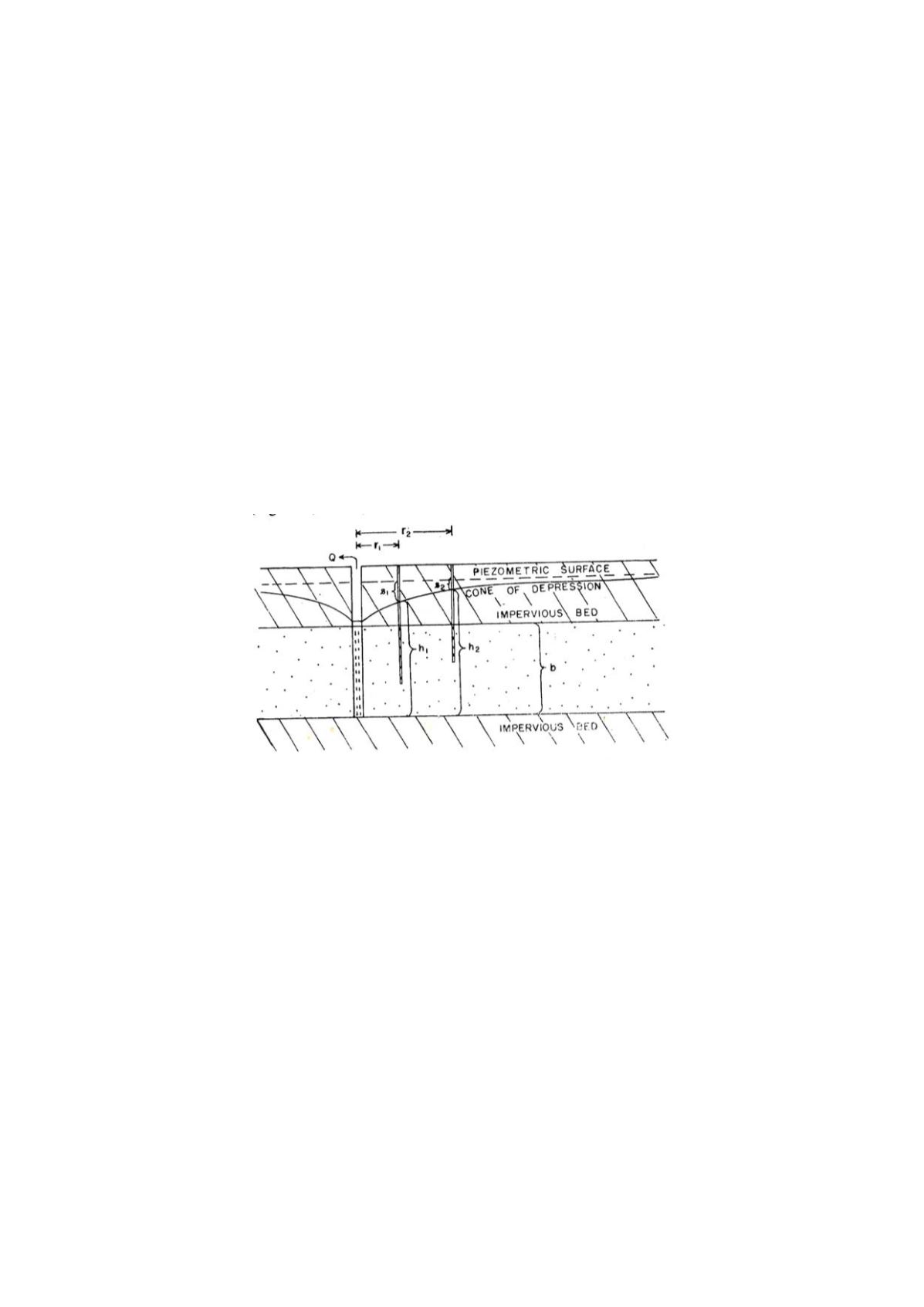
When a well is pumped, water is removed from the aquifer surrounding the
well, and the water table or piezometric surface, depending on the aquifer, is
lowered. The drawdown at a given point is a distance the water table is lowered
(Figure 6.4). The drawdown curve, plotted based on observation well installed
away from the pumped well, shows variation or drawdown with distance from
the pumped well.
Fig. 6.4 : Cross section of confined aquifer and piezometric surface
(After Karanth, 2004)
Determination of 'T' for confined aquifer
Steady state and constant discharge :
When a pumped well penetrates the entire thickness of a confined aquifer, Theim's
equations applied to determine the value of 'T'. Two observation wells are
installed at a distance of r1 and r2 and the well is pumped at a constant rate
until the drawdown reached a steady state. The values of drawdowns are
measured at regular intervals and are recorded. The values of drawdowns are
generally not taken from the pumped well because of well loss etc. 'T' can be
calculated from the following equations:


