[ 50 ]
“SHG
S
,
SAVING
FOR
THE
PRESENT
,
SECURING
THE
FUTURE
”
SHARE OF MODERN AGENCIES IN CREDIT OUTSTANDING
Perhaps as a response, during late 1980s and early 1990s, several Non-
Governmental Organisations made forays into microfinance and brought several
innovations to reach the unreached. Group approach through self-help groups
(SHG)
4
was one of the most important channels for reaching the unreached to
provide financial access. With policy support from Reserve Bank of India (RBI)
and NABARD, the Self Help Group-Bank Linkage Programme (SHG-BLP) was
launched during early 1990s, which has completed 25 years as of now. Apart
from SHG Bank Linkage channel, there has been emergence of Microfinance
Institutions (MFIs) on the rural finance scene. Though the share of MFIs and
SHGs in the total credit outstanding for a rural household is not substantial
compared to mainstream institutions, the 25-year journey of SHG-BLP, mostly
covering women, has been phenomenal as will be discussed in the next section.
Undisputedly, the programme has been a movement that empowered women.
The model has been accepted widely as an effective delivery mechanism for
most services. Thus, the influence of the SHG movement has been well beyond
mere providing financial resources to the rural people transcending to rural
health, education, and caring for the environment.
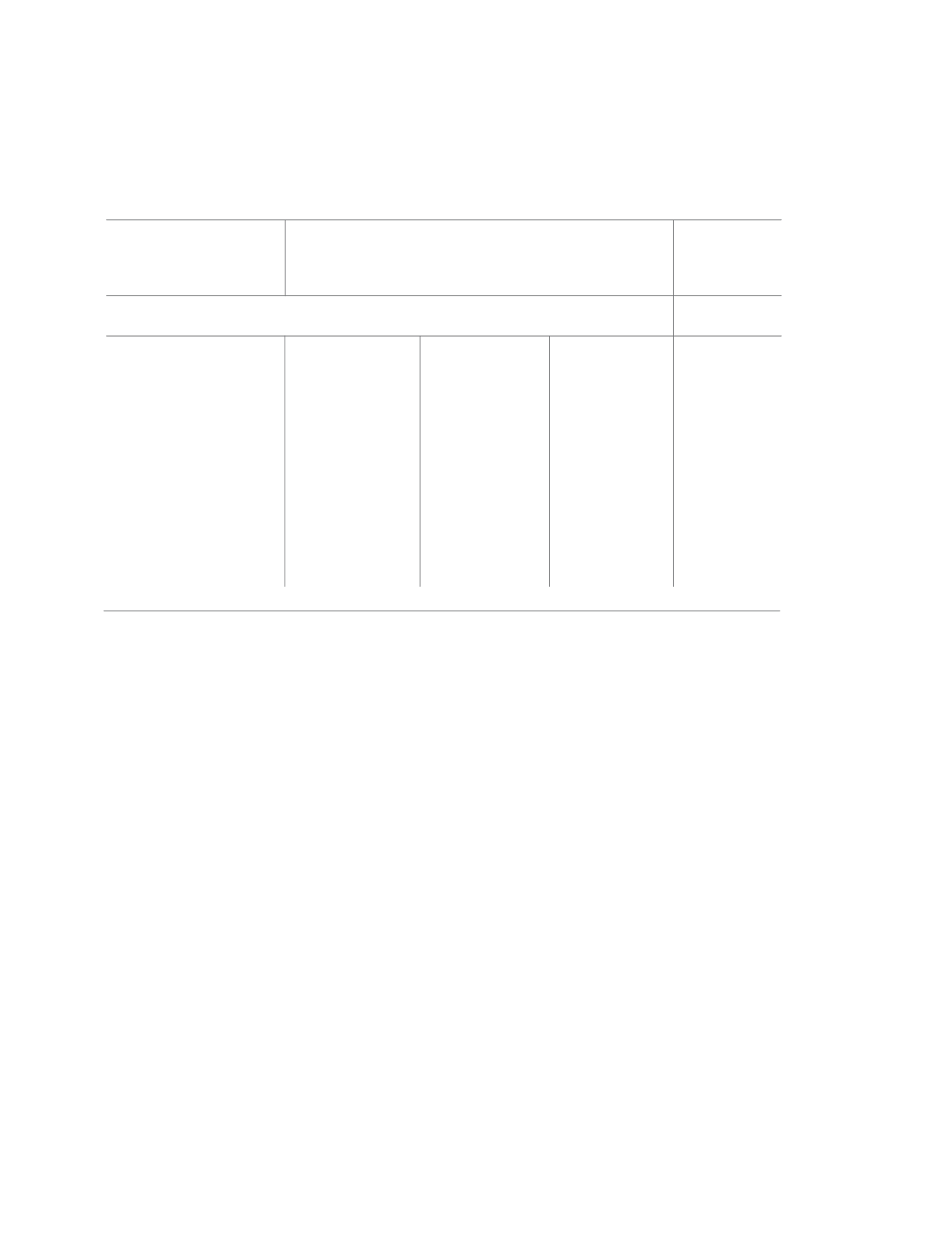
Table 2.
SHARES OF TRADITIONAL AND MODERN
INSTITUTIONAL AGENCIES# IN TOTAL CREDIT
OUTSTANDING, RURAL, 2012
Credit Agency
Formal
Agencies
Informal
Agencies
Traditional
Modern
Others
All India
51.1
4.2
44.0
0.7
38.7
10.8
49.3
1.2
24.0
54.9
4.1
38.5
2.5
52.3
4.7
42.6
0.4
43.5
6.8
49.6
0.1
33.7
8.3
0.1
8.3
7.3
68.3
0.4
West Bengal
Telangana
Tamil Nadu
Odisha
Karnataka
Andhra Pradesh
Source: Compiled from NSS Report No.577: Household Indebtedness in India
Note: # in Table 1.


