
- 1. India and the World: The Economy in FY2024
- 2. Cooperatives: Tackling Challenges, Building Opportunities
- 3. Investing in a Sustainable Tomorrow
- 4. Towards Inclusive Development
- 5. Financing Rural Infrastructure for Sustainable Development
- 6. Credit Planning and Delivery for Financial Inclusion
- 7. Supervisory Role of NABARD
- 8. Empowering Rural Financial Institutions
- 9. People—Processes and Policies
- 10. Leveraging Finance for Growth
- Success Stories
- Board of Directors as on 31 March 2024 (PDF)
- Principal Officers (PDF)
- Corporate Governance (PDF)
- Annual Accounts 2023–24 (PDF)
- E-Mail Addresses of HODs and Subsidiaries at Mumbai (PDF)
- Regional Offices/Cells/Training Establishments/Subsidiaries (PDF)
- Annual Report 2023-24 (PDF)
- Home
- Board of Directors as on 31 March 2024 (PDF)
- Principal Officers (PDF)
- 1. India and the World: The Economy in FY2024
- 2. Cooperatives: Tackling Challenges, Building Opportunities
- 3. Investing in a Sustainable Tomorrow
- 4. Towards Inclusive Development
- 5. Financing Rural Infrastructure for Sustainable Development
- 6. Credit Planning and Delivery for Financial Inclusion
- 7. Supervisory Role of NABARD
- 8. Empowering Rural Financial Institutions
- 9. People—Processes and Policies
- 10. Leveraging Finance for Growth
- Success Stories
- Corporate Governance (PDF)
- Annual Accounts 2023–24 (PDF)
- E-Mail Addresses of HODs and Subsidiaries at Mumbai (PDF)
- Regional Offices/Cells/Training Establishments/Subsidiaries (PDF)
- Annual Report 2023-24 (PDF)
Investment in infrastructure has a multiplier effect on growth and employment in an economy. Rural infrastructure development strongly figures in the government’s plans and policies to map the Indian landscape on the basis of connectivity and logistics. Intra-regional infrastructure to integrate rural areas with nearby urban centres can transform India’s growth trajectory.
Figure 5.1: NABARD-managed infrastructure funds for rural India as on 31 March 2024 (₹ crore)
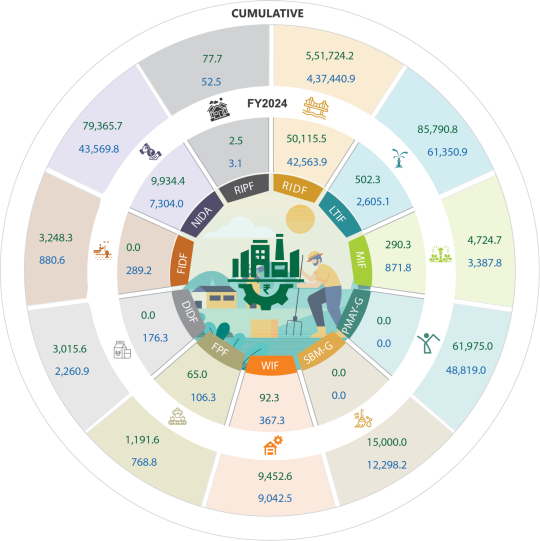
DIDF = Dairy Processing and Infrastructure Development Fund, FIDF = Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund, FPF = Food Processing Fund, LTIF = Long Term Irrigation Fund, MIF = Micro-Irrigation Fund, NIDA = NABARD Infrastructure Development Assistance, PMAY-G = Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana-Gramin, RIDF = Rural Infrastructure Development Fund, RIPF = Rural Infrastructure Promotion Fund, SBM-G = Swachh Bharat Mission-Grameen, WIF = Warehouse Infrastructure Fund.
Robust and reliable rural infrastructure to support modern agriculture, improved irrigation, enhanced rural connectivity, better market access, more renewable energy, and quality education and health is vital for enhancing production, consumption, and trade of goods and services. This, in turn, will lead to more sustainable rural livelihoods in India.
NABARD plays a crucial role in facilitating the financing, promotion, and sustainable development of rural infrastructure. It provides technical assistance and financial support for the construction of rural roads, irrigation systems, warehousing facilities, and renewable energy installations by leveraging various funds vested in it. The cumulative funds sanctioned by NABARD till FY2024 under infrastructure financing stood at ₹8.2 lakh crore while disbursements added up to ₹6.2 lakh crore (Figure 5.1).
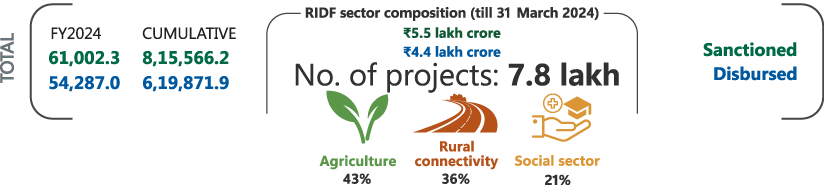
Figure 5.2: Performance of RIDF as on 31 March 2024
5.1 RURAL INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPMENT FUND1
The Rural Infrastructure Development Fund (RIDF) (instituted in 1996) aims to support public investment, given the shortfall of priority sector lending, thus bridging the rural–urban infrastructure gap towards promoting inclusive rural growth and socioeconomic development.
5.1.1 Trends and patterns
During FY2024 (RIDF Tranche XXIX), NABARD received an allocation of ₹40,474.6 crore under RIDF (2.4% increase over FY2023) and sanctioned ₹50,115.5 crore towards financing rural projects in agriculture and related activities, irrigation, social sector, and rural connectivity (Figure 5.2).
5.1.2 Output>>Outcomes>>Impact
Over the decades, RIDF has played a significant role in financing rural infrastructure projects across India, contributing to improved rural connectivity and agricultural productivity (Figure 5.3, Showcase 5.1).
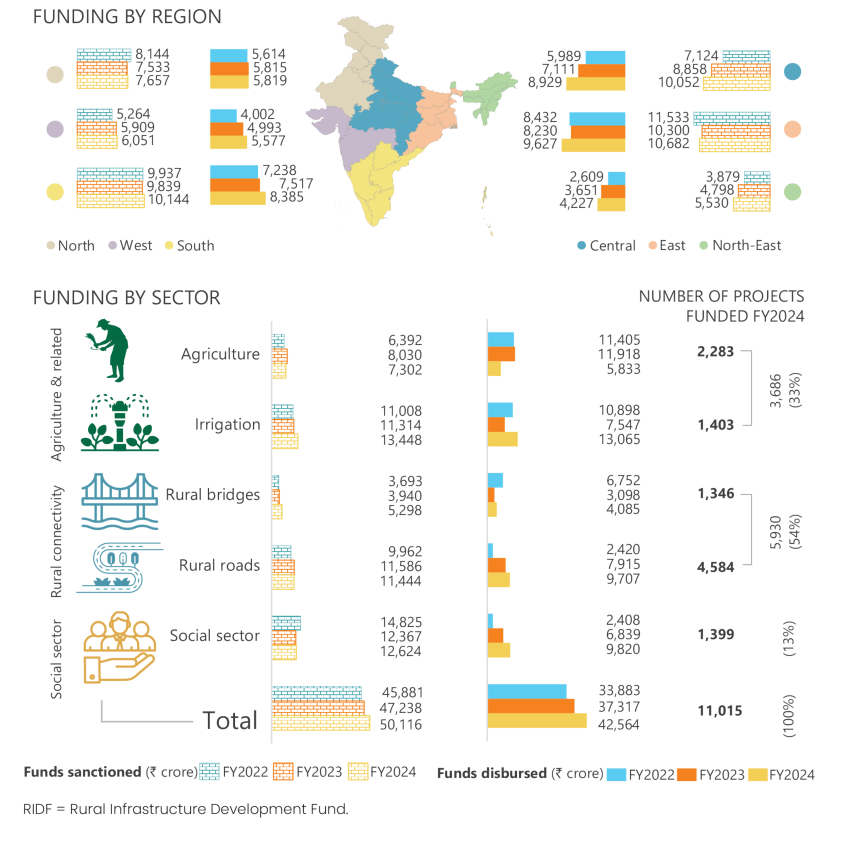
Figure 5.3: Outputs and outcomes under RIDF as on 31 March 2024
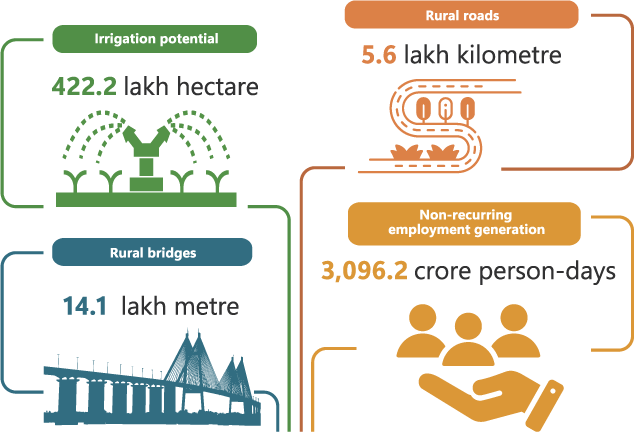
RIDF = Rural Infrastructure Development Fund.
Showcase 5.1: Augmenting irrigation facilities in rainfed areas of Bundelkhand
Project: Providing irrigation facilities in rainfed areas
Location: 15 villages of Babina block, Jhansi district, Bundelkhand region, Uttar Pradesh
Implementing agency: Irrigation and Water Resource Department, Government of Uttar Pradesh
Total financial outlay: ₹246.8 crore
NABARD assistance: ₹146.2 crore
Challenge addressed: Irrigation in drought-prone villages not within the command of any other project.
Intervention
- A pump house was constructed upstream of the Sukwan–Dukhwan on the left bank of the Betwa river.
Output>>Outcomes>>Impact
- Culturable command area created: 5,799 hectare
- Number of villages benefitted: 15

Construction of pump house and canal system
Impact evaluation studies on RIDF projects have indicated improvements in rural socioeconomic conditions and rise in credit demand within project areas (Box 5.1). Additionally, these studies have shown a diversification of lending portfolios, growth in deposits, and expansion of bank branch networks, contributing to enhanced financial inclusion. Furthermore, the investments and interventions have led to better rural health benefits, which have not just reduced rural health care expenses but also resulted in a more productive rural workforce.
5.1.3 New initiatives in FY2024
NABARD contributed to the state share of flagship GOI schemes by sanctioning projects worth ₹5,155 crore under Jal Jeevan Mission, ₹1,063 crore under Pradhan Mantri Kusum Yojana, and ₹617 crore towards the installation of 20,000 solar powered pump sets under the Saur Sujala Scheme in Chhattisgarh.
During the year, the RIDF portal underwent changes such as the introduction of an appraisal and disbursement module and monitoring through geo map.
5.2 RURAL INFRASTRUCTURE PROMOTION FUND
Financial assistance is provided under Rural Infrastructure Promotion Fund (RIPF) for the building of innovative, experimental, or promotional last mile rural infrastructure and rural capacity building initiatives.
As on 31 March 2024, cumulative sanctions under RIPF stood at ₹77.7 crore and disbursements at ₹52.5 crore.
Box 5.1: RIDF-supported social sector projects: Impact evaluation by IIT Kharagpur
1. Impact evaluation of rural drinking water supply project in Odisha indicated
- increased availability of water,
- decreased use of surface water sources for drinking,
- reduced time allocation by women to the task of fetching water,
- improved hygiene practices,
- reduced open defecation,
- decreased water-borne diseases, and
- improved health and wellbeing with increased economic activities.
2. Impact evaluation of anganwadi project in West Bengal indicated improvements in
- school attendance;
- health check-ups of children, as also pregnant and nursing mothers;
- awareness level, knowledge, and skills;
- access to nutritious food and safe drinking water;
- cleanliness of the surroundings; and
- frequency of bank transactions, use of ATM cards, institutional savings and availment of bank loans.
Food habits and nutritional status of the children, hygiene levels, drinking water and sanitation facilities, and quality of awareness building and education delivery at the centres could be improved further.
IIT = Indian Institute of Technology, RIDF = Rural Infrastructure Development Fund.
Showcase 5.2: Time-controlled automated sprinkler irrigation system for greenhouse cultivation
Project: Time-controlled automated sprinkler irrigation system for greenhouse cultivation
Location: South Sikkim (Namchi) district, Sikkim
Implementing agency: Agricultural Technology Management Agency, Sikkim
Total financial outlay: ₹5.4 lakh
NABARD assistance: ₹4.8 lakh
Challenge: Improving water-use efficiency in dry area for higher production and yield.
Intervention: Automated time-based irrigation systems optimising soil moisture using sensor and pump set up in greenhouses for horticulture and floriculture.
Beneficiaries: Five flower growers
Output>>Outcomes>>Impact
- 30%–40% water saved.
- Improvement in foliar growth, quality of flowers, plant health, root growth, etc.
- Savings in time and effort due to automated system.


Poly house
5.3 LONG TERM IRRIGATION FUND2
The Long-Term Irrigation Fund (LTIF) funding arrangement has been extended up to FY2026 for state governments for 60 ongoing projects under the Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme and 85 projects under Command Area Development and Water Management with Government of India interest subvention up to 2%.
Figure 5.4: Performance of the LTIF
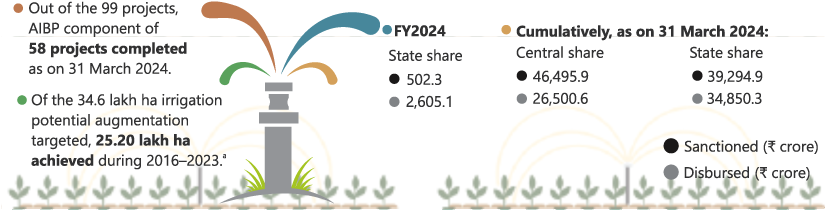
aAs shared by Ministry of Jal Shakti, Government of India.
AIBP = Accelerated Irrigation Benefit Programme, LTIF = Long Term Irrigation Fund
5.4 MICRO-IRRIGATION FUND3
Micro Irrigation Fund (MIF) was announced in the Union Budget for FY2020 endowed with the initial corpus of ₹5,000 crore, to be operationalised by NABARD for the period FY2020–FY2024.
Figure 5.5: Performance of MIF as on 31 March 2024
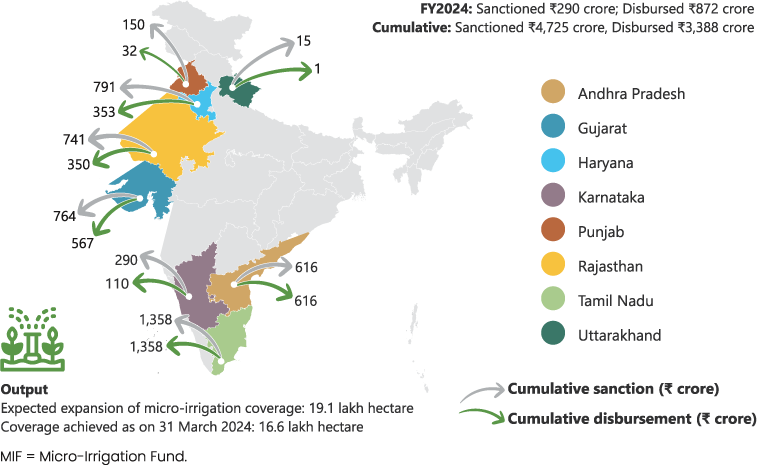
The objective of MIF is to support state governments in mobilising additional resources to expand micro-irrigation coverage and encourage its adoption beyond the provisions of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana—Per Drop More Crop.
5.5 NABARD INFRASTRUCTURE DEVELOPMENT ASSISTANCE4
NABARD Infrastructure Development Assistance (NIDA) offers flexible long-term loans to state governments, well-managed public sector entities, and other eligible entities for financing rural infrastructure. Through NIDA, NABARD has been contributing to the creation of key
Figure 5.6: Performance of NIDA as on 31 March 2024
FY 2024, term loan sanctioned: ₹9,934.4 crore
Cumulative: 153 projects with sanctioned term loan of ₹79,365.7 crore (including for withdrawn projects)
Amount disbursed till 31 March 2024: ₹43.569.8 crore
Cumulative term loan sanctioned by sector (amount in ₹ crore)
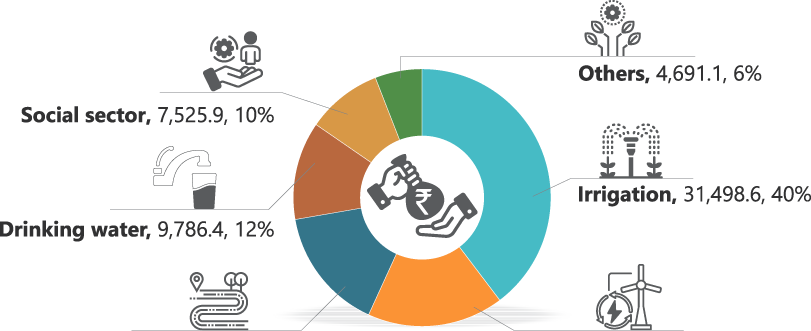
NIDA = NABARD Infrastructure Development Assistance
Notes:
- Social sector includes health, education, rural housing, rural tourism, anganwadis, and old age homes.
- Others include agricultural marketing, warehousing, watershed development, communication, sewerage, etc.
infrastructure and improving the quality of life in rural India. The scope for funding has further broadened with the inclusion of public–private partnership (PPP) and non-PPP projects to be undertaken by registered entities like corporates/companies, cooperatives, etc.
Figure 5.7: Expected outcomes of projects funded under NIDA
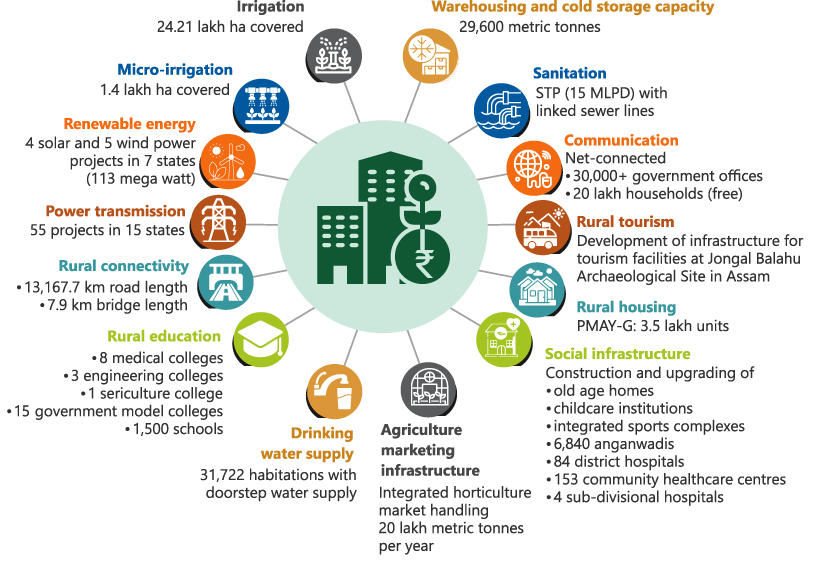
ha = hectare, MLPD = million litres per day, NIDA = NABARD Infrastructure Development Assistance, PMAY-G = Pradhan Mantri Awaas Yojana–Gramin, STP = sewage treatment plant.
Showcase 5.3: Narmada–Kshipra Link Multipurpose Project
Project: Narmada–Kshipra Link Multipurpose Project, Madhya Pradesh
Location and challenge: Inter-basin water transfer through piped irrigation network to water scarce areas of upper Chambal basin.
Total financial outlay: ₹1,856.7 crore
NIDA term loan: ₹1,745.8 crore
Output>>Outcomes>>Impact
- Irrigation facilities extended to 30,000 hectare in 162 villages across Ujjain and Shajapur districts, enhancing crop yield.
- Quality drinking water supply to over 1.5 million people.
- Diversification to high-value hybrid crops like wheat, maize, gram, and other horticulture crops.
- Rise in farmers’ income up to ₹77,015 per hectare reducing rural–urban migration.

Narmada–Kshipra Link Multipurpose Project, Madhya Pradesh
5.6 POST-HARVEST INFRASTRUCTURE
NABARD has been offering loans and subsidies for setting up post-harvest infrastructure such as warehouses, cold storage facilities, processing units, packaging centres, etc., (Figures 5.8–5.10).
5.6.1 Warehouse Infrastructure Fund5
NABARD extends financial assistance through the Warehouse Infrastructure Fund (WIF) to state governments, state-owned agencies, and corporate entities to systematically enhance warehouse capacity, thereby strengthening agricultural value chains. The investment through WIF plays a pivotal role in facilitating and enhancing farmers’ access to finance through negotiable warehouse receipts (NWR).
Figure 5.8: Sanctions and disbursements under WIF as on 31 March 2024 (₹ crore)
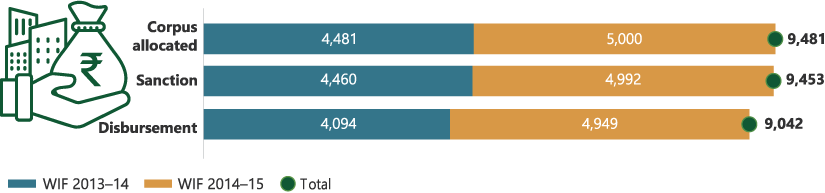
WIF = Warehouse Infrastructure Fund. Note: For WIF 2013–14, out of a corpus of ₹5,000 crore, ₹519 crore was refunded to commercial banks
Figure 5.9: Region-wise performance of WIF as on 31 March 2024
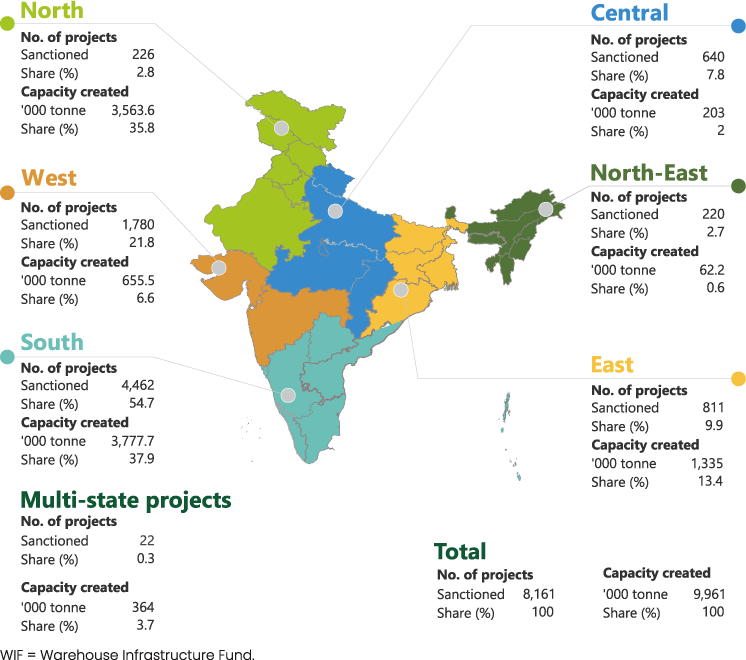
Figure 5.10: Output under WIF as on 31 March 2024
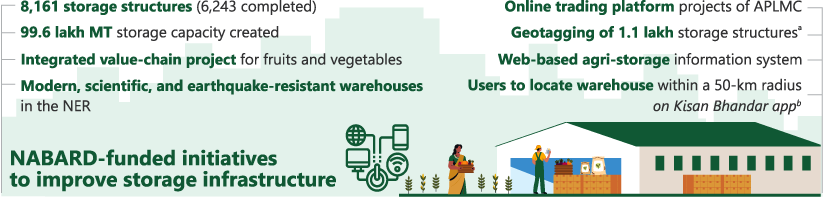
aThese storage structures have been geotagged and linked to a centralised database which can be ported with other platforms like e-NAM to create an integrated portal.
bThe app is being further developed to help farmers know the availability of the space in the agri-storage infrastructure, improve booking and payment facilities, and integration with other website/apps such as payment gateways, bank branch location, etc.
APLMC = Agricultural Produce and Livestock Market Committee, e-NAM = e-National Agriculture Market, km = kilometre, MT = metric tonne, NER = North-Eastern Region, WIF = Warehouse Infrastructure Fund.
5.6.2 Food Processing Fund6
India’s food processing sector is one of the largest in the world with a projected output of $535 billion by FY2026.7
The development of the food processing industry is essential for enhancing food security, reducing post-harvest losses, generating employment, stimulating economic growth, and meeting the evolving needs of consumers in both domestic and international markets. NABARD’s Food Processing Fund (FPF) has been instrumental in mitigating food wastage, broadening value addition, and establishing connections between farmers and consumers. NABARD has committed ₹1,191.6 crore as financial assistance up to FY2024 for projects spanning 17 states, including NER states like Assam, Manipur, and Meghalaya.
Figure 5.11: NABARD-supported food processing infrastructure as on 31 March 2024

Showcase 5.4: Unveiling a mega food park in Himachal Pradesh
Project: Cremica Mega Food Park
Implementing agency: Cremica Food Park Pvt Ltd
Term loan sanctioned: ₹40.2 crore
Location: Haroli, Una district, Himachal Pradesh.
Progress
- The mega food park has an area of 52 acres, of which 23.8 acres is leasable area.
- Entire land is already under possession of the implementing agency and is notified for industrial use.
- The following infrastructure has been completed in the core processing centre:
- Frozen cold store (four stores of 150 MT capacity each)
- Warehouse raw material (3,000 square metre)
- Sewage treatment plant (1.2 million litre per day)
- The construction of a primary processing centre in Solan, Himachal Pradesh is complete.
- Following independent units have set up their manufacturing facility in the food park, which are operational: NEC Retroflex, Trustable Food India Pvt Ltd, Una Miricle Food, and Nijjer Foxtale Con.
Output >> Outcomes >> Impact
- Due to sale/lease of plots, the food park is reporting profits from its own operations.
- The entrepreneurs are optimistic that the Cremica Mega Food Park will be a harbinger of progress for the food processing industry of Himachal Pradesh.
- The Cremica Mega Food Park will potentially maximise value addition, minimise wastage, increase farmer’s income, and create employment opportunities to 8,500 people, particularly in rural sector.
- The mega food park links agricultural produce (potato, tomato, fruits, and meat) to the market by bringing together farmers, processors, and retailers to ensure maximising value addition and food processing.
5.6.3 New initiatives during FY2024 in post-harvest infrastructure
- NABARD’s senior officials deputed to the Working Group constituted by the Warehousing Development and Regulatory Authority (WDRA) have provided technical assistance in developing a digital gateway platform for promotion of e-NWR-based pledge financing for the benefit of small and marginal farmers and traders.
- NABARD has initiated the process of developing the Dynamic Kisan Bhandar App and associated web-based portal for facilitating access of small and marginal farmers to geotagged storage spaces, thereby reducing post-harvest losses. NABARD Consultancy Services has been brought in as the consultancy firm to develop the mobile application.
5.7 OTHER INFRASTRUCTURE INITIATIVES
5.7.1 Dairy Processing and Infrastructure Development Fund8
The Dairy Processing and Infrastructure Development Fund (DIDF) was vested with NABARD in FY2018 for the creation and modernisation of milk processing facilities and development of other dairy-related infrastructure, with initial corpus of ₹8,004 crore and implementation period up to FY2023.
Figure 5.12: Performance of DIDF as on 31 March 2024
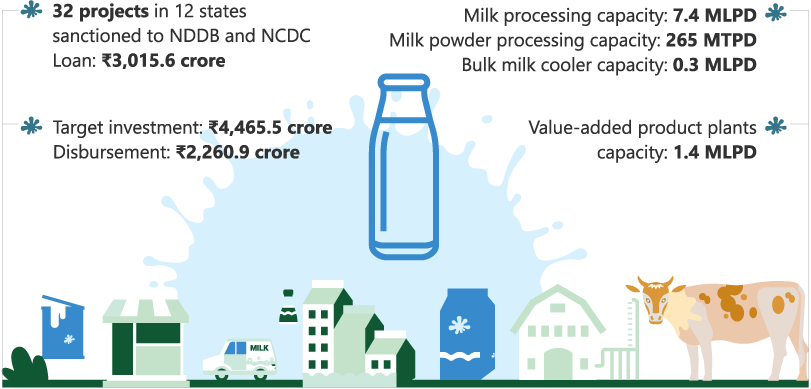
DIDF = Dairy Processing and Infrastructure Development Fund, MLPD = million litres per day, MTPD = metric tonnes per day, NCDC = National Cooperative Development Corporation, NDDB = National Dairy Development Board.
5.7.2 Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund9
As per the Union Budget FY2019, the Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF) was established (with NABARD as one of the nodal loaning entities) with a total corpus of ₹7,522.5 crore, spanning a lending period of 5 years from FY2019 to FY2023. The scheme has since been extended till 31 March 2026.
Figure 5.13: Performance of FIDF as on 31 March 2024
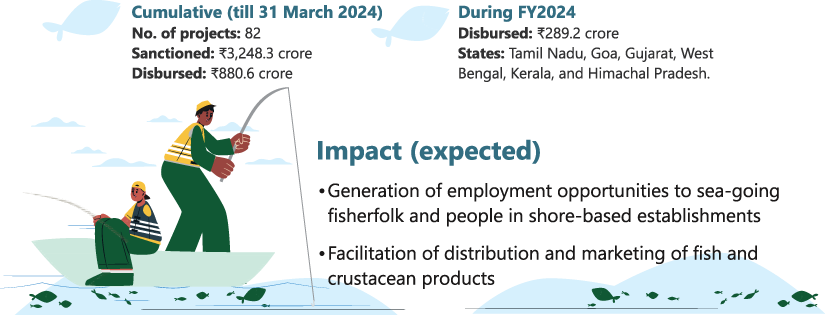
Tripartite Memoranda of Agreement with 12 state governments/Union Territories—
Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Goa, Odisha, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, and Haryana.
FIDF = Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund.
Showcase 5.5: Construction of fishing harbour at Tharangambadi in Mayiladuthurai District, Tamil Nadu
Project: Construction of fishing harbour
Location: Tharangambadi in Mayiladuthurai district, Tamil Nadu
Funding
- Project outlay: ₹120 crore
- A term loan of ₹108 crore availed by the Government of Tamil Nadu from NABARD in February 2020.
Challenges addressed
- Fishing is the primary source of livelihood for 10 coastal villages near Tharangambadi in Mayiladuthurai district. The fishing community suffered severe losses during natural disasters, particularly during the 2004 Indian Ocean Tsunami and 2018 Gaja cyclone.
- The fisherfolk had been experiencing difficulties in berthing their boats due to the non-availability of infrastructure.

Tharangambadi fishing harbour site
Intervention
- The fishing harbour completed in May 2023 is designed to facilitate the berthing of 800 fibre boats and 225 mechanised boats.
- Other infrastructure facilities include breakwaters structures on both the northern and southern ends of the harbour for boats to enter and exit, slipway, a fish auctioning yard, a fishing net mending shed, an overhead water tank, freshwater sump, vehicle parking area, public toilets, administrative and security buildings, etc.
Output>>Outcomes>>Impact (expected)
- Fisherfolk from Chinnamedu, Vellakoil, Chinnangudi, Kuttiyandiyur, Thazhampettai, Pudupettai, Chandrapadi, Perumalpettai, and Chinnoorpettai can use the new harbour.
- The socioeconomic status of fisherfolk from these villages is expected to improve substantially.
- Additional employment is likely to be generated for
- 3,975 sea-going fisherfolk,
- 2,000 others employed in shore-based establishments, and
- those engaged in distribution and marketing of fish and crustacean products.
- The average annual landing of fish and crustacean of 29,025 tonnes is valued at ₹380.3 crore.
- Fisherfolk can go fishing throughout the year and fully exploit the under-utilised fishery resources.
5.7.3 Rural Infrastructure Assistance to State Governments
Under the initiative ‘Renewed Engagements with State Governments for Infrastructure Financing’, Rural Infrastructure Assistance to State Governments is being revamped to realign with requirement of state governments in the eastern region and aspirational districts in other states for creating infrastructure that supports rural livelihoods.
5.8 WAY FORWARD
The synergy between physical and digital infrastructure is essential for building resilient, efficient, and inclusive infrastructure systems that support sustainable development, foster innovation, and enhance quality of life for people around the world.
NABARD is in the process of developing policy guidelines for working capital financing and development of exclusive short-term working capital financing products which can facilitate composite loan assistance to prospective entrepreneurs willing to set up food processing units outside the designated food parks. It is also exploring the possibility of collaboration with financial and banking institutions, viz. commercial banks, regional rural banks, and cooperative banks, for providing working capital finance assistance.
The effectiveness of RIDF support may be enhanced by extending financial assistance to PPP projects and catalysing private sector investment in rural infrastructure development, contributing to sustainable economic growth, poverty reduction, and ensuring holistic development of rural areas.
Innovations in infrastructure financing are essential for mobilising capital, unlocking investment opportunities, and accelerating infrastructure development. Such innovative financing solutions are bound to play a crucial role in addressing infrastructure gaps, promoting sustainable development, and building resilient and inclusive infrastructure systems for the future.
NOTES
- https://www.nabard.org/content1.aspx?id=573&catid=8&mid=8.
- https://www.nabard.org/content1.aspx?id=655&catid=8&mid=8.
- https://www.nabard.org/content1.aspx?id=1720&catid=8&mid=8.
- https://www.nabard.org/content1.aspx?id=2800&catid=8&mid=8.
- https://www.nabard.org/content1.aspx?id=571&catid=8&mid=8.
- https://www.nabard.org/content.aspx?id=570.
- India’s food processing sector poised to reach $535 billion by 2025-26, Economic Times, 7 April 2024. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/indias-food-processing-sector-poised-to-reach-535-billion-by-2025-26/articleshow/109102067.cms?from=mdr
- https://dahd.nic.in/schemes/programmes/didf.
- https://www.fidf.in/
© 2024 NABARD All Rights Reserved
Designed & Developed by RDX Digital
