422
In fact, the relationship is inverse as between the asset sizes, on the
one hand, and institutional and non-institutional sources, on the other
(Table 5)
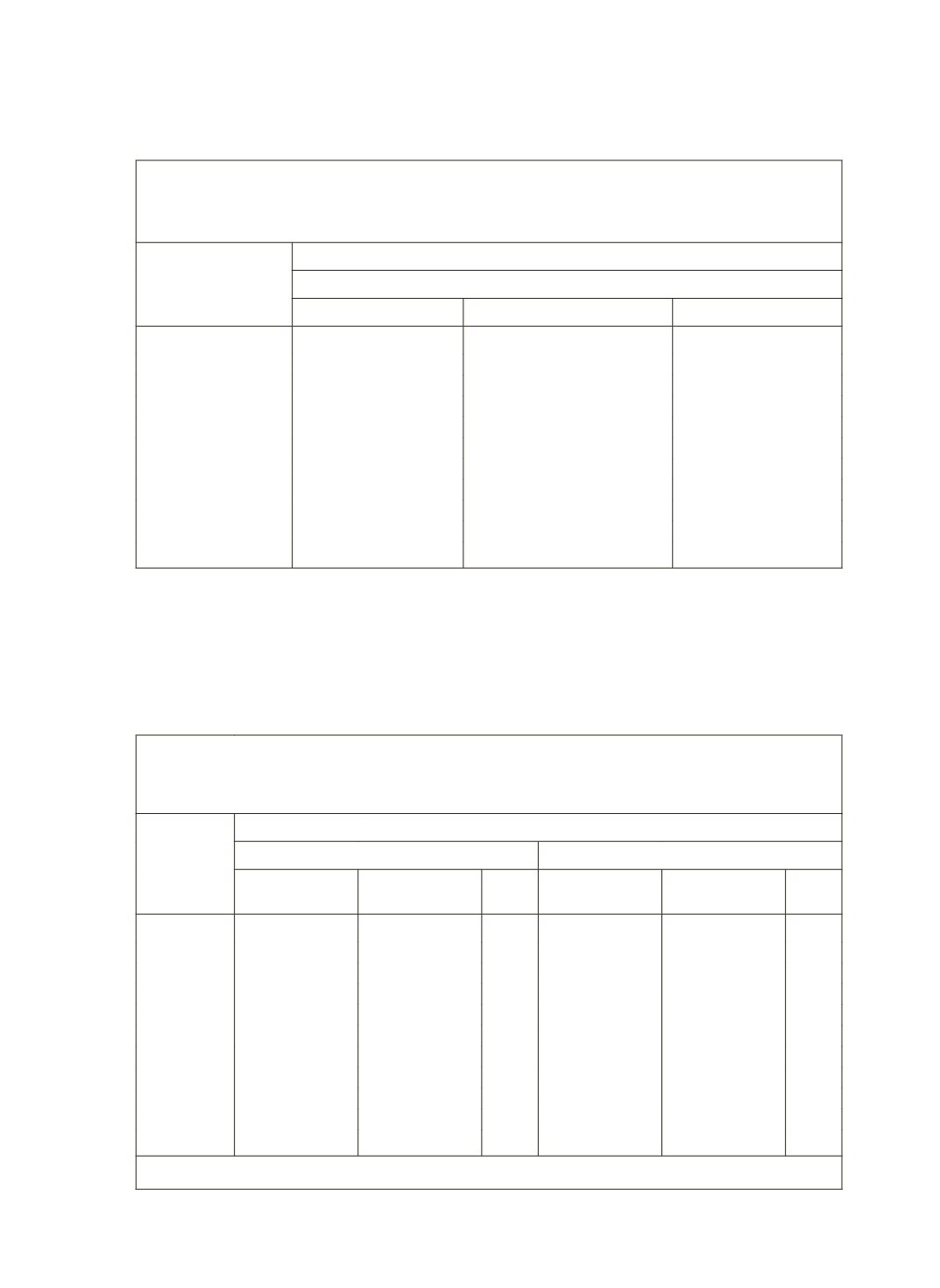
Table 5: Percentage Share of Institutional Agencies to the Total
Cash Debt of the Households as on 30-6-2002 by Household
Assets Holding Class (AHC)
AHC
(
`
000)
Percentage Share
Rural
Institutional
Non-Institutional
All
< 15
21.0
79.0
100.0
15-30
29.0
71.0
100.0
30-60
31.0
69.0
100.0
60-100
31.0
70.0
100.0
100-150
39.0
61.0
100.0
150-200
42.0
58.0
100.0
200-300
48.0
52.0
100.0
300-450
59.0
42.0
100.0
450-800
67.0
33.0
100.0
800 +
80.0
21.0
100.0
All
57.0
43.0
100.0
(ii)
Looking at it differently, the incidence of indebtedness (in terms of the
percentage of indebted rural households) to institutional agencies is
just one-fourth to one-half of that to non-institutional agencies amongst
the low asset classes (Table 6). Contrariwise, the high asset groups have
low incidence to non-institutional agencies.
Table 6: Incidence of Indebtedness (IOI) of Households as on
30-06-2002 to Institutional and Non-Iinstitutional Credit
Agencies by Household Assets Holding Class(AHC)
AHC
(
`
000)
IOI (%) to
Rural
Urban
Institutional
Non-
Institutional
All
Institutional
Non-
Institutional
All
< 15
03.6
12.0 15.0
1.4
9.5 10.7
15-30
6.2
13.9 19.0
2.4
12.8 14.8
30-60
8.7
17.7 25.2
4.5
11.0 14.8
60-100
10.9
17.7 26.5
7.2
11.9 18.3
100-150
13.6
17.9 28.9
8.3
12.2 19.7
150-200
14.6
17.1 28.7
8.9
12.0 20.0
200-300
16.2
15.7 28.7
11.1
10.1 19.9
300-450
18.7
13.2 28.7
12.1
8.2 18.7
450-800
22.0
13.0 31.0
16.9
7.2 22.5
800 +
26.7
10.3 32.9
18.5
4.2 21.4
All
13.4
15.5 26.5
9.3
9.4 17.8
Source:
NSSO(2005), Household Indebtedness in India as on 30-06-2002, Report No.501(59/18.2/2)


